Mattress Matchmaker for Insomnia
This tool helps you find the best mattress type for insomnia based on your specific sleep needs. Enter your sleep position, body weight, and temperature preferences to get personalized recommendations.
Recommended Mattress Type
Ideal Firmness
3-5Why It Works
Insomnia Relief Features
Struggling to stay asleep night after night? The surface you lie on can be a silent game‑changer. Picking the right mattress for insomnia isn’t just about comfort - it’s about creating an environment that supports uninterrupted rest.
Key Takeaways
- Mattress firmness, material, and motion isolation directly affect sleep continuity.
- Memory foam and hybrid models usually score highest for temperature regulation and pressure relief.
- Match mattress type to your sleep position and personal temperature preferences.
- Test at home for at least 15 minutes in your typical sleep posture before buying.
- Consider warranty length and trial period as part of the total cost.
When building a healthier night, start with the basics.
Mattress is a supportive surface designed to distribute body weight, align the spine, and cushion pressure points while you sleep. It comes in several construction styles, each with distinct performance traits. Insomnia refers to difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non‑restorative sleep for at least three nights a week over a month. Chronic insomnia can worsen stress, lower immune function, and increase accident risk.Why Your Mattress Matters for Insomnia
Research from the National Sleep Foundation shows that 30% of people who report chronic insomnia also cite an uncomfortable mattress as a contributing factor. A mattress that’s too soft allows the hips to sink, causing the spine to curve and trigger micro‑awakenings. Conversely, an overly firm surface creates pressure on shoulders and hips, leading to tossing and turning.
Two physiological mechanisms are most relevant:
- Pressure‑point relief: Reducing localized stress helps the body stay in a relaxed state, preventing the sympathetic nervous system from kicking back in.
- Temperature regulation: A mattress that breathes keeps core body temperature stable, lowering the chance of waking up from overheating.
Common Mattress Types and Their Insomnia‑Friendly Traits
Below is a quick snapshot of the main constructions you’ll encounter. Each type varies in firmness range, motion isolation, and temperature control.
| Type | Typical Firmness | Best for Insomnia? | Motion Isolation | Temperature Control | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory Foam | Medium‑soft to medium | Yes - excellent pressure relief | High | Moderate (gel or open‑cell helps) | $500‑$2000 |
| Innerspring | Medium‑firm to firm | No - limited motion isolation | Low‑moderate | Good (airflow through coils) | $300‑$1500 |
| Latex | Medium to firm | Yes - responsive support, natural breathability | Moderate | High (natural latex is cool) | $800‑$2500 |
| Hybrid (foam + coils) | Medium‑soft to medium‑firm | Yes - balances contour and bounce | High | High (coil airflow + foam comfort) | $1000‑$3000 |
To give each material a proper identity, we’ll define the most popular variants.
Memory Foam is a viscoelastic polymer that conforms to body shape under heat, distributing weight evenly and minimizing pressure points. It often includes gel or copper infusions to counteract heat retention. Innerspring refers to a network of steel coils that provide bounce and support, usually topped with a thin comfort layer. Coils vary from traditional Bonnell to pocket‑spring designs. Latex is a natural or synthetic rubber material prized for its elasticity, durability, and breathability. Natural latex tends to be cooler and hypoallergenic. Hybrid combines foam layers (memory or latex) with pocketed coils, aiming to deliver both contouring comfort and responsive support. Firmness measures how soft or hard a mattress feels, usually rated on a 1‑10 scale where 1 is ultra‑soft and 10 is rock‑solid.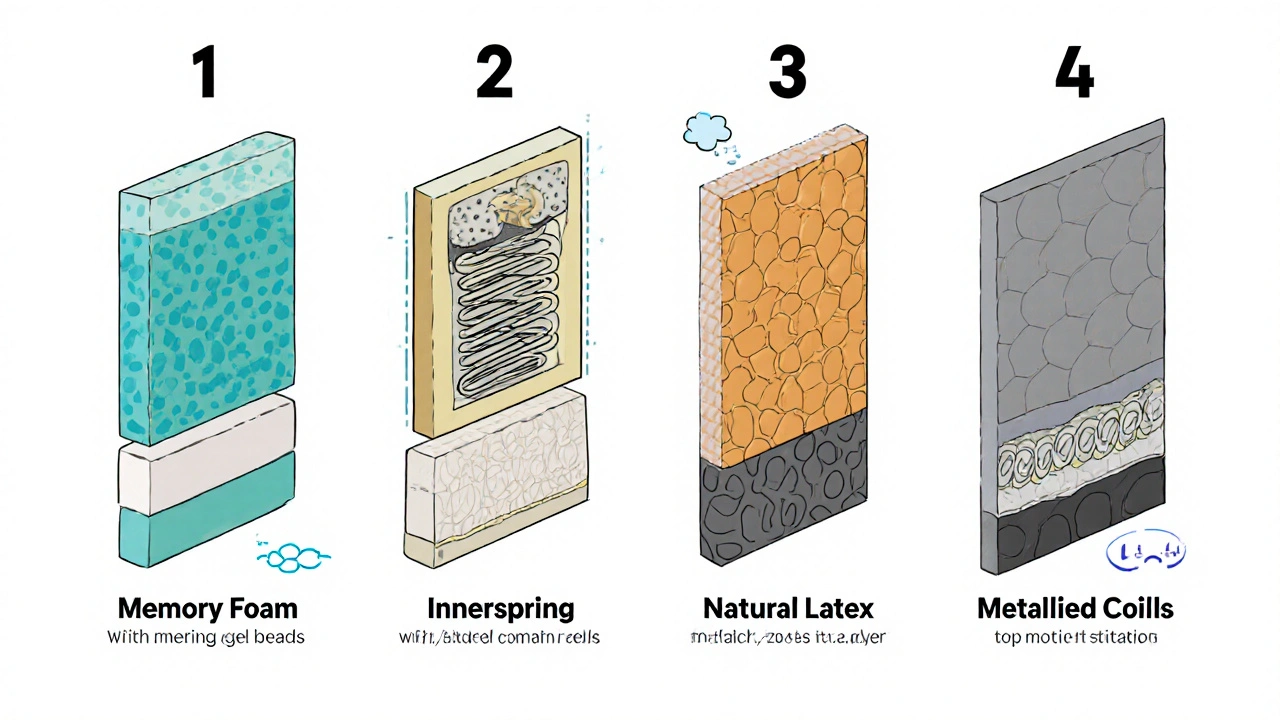
Match Mattress Features to Your Sleep Profile
Everyone’s body is different, so a one‑size‑fits‑all approach rarely works. Consider three core factors:
- Sleep position: Side sleepers need more contour (medium‑soft), back sleepers benefit from medium support, and stomach sleepers usually require a firmer surface.
- Body weight: Heavier individuals often feel more stable on a slightly firmer mattress, while lighter sleepers may appreciate the sink of softer foam.
- Temperature preference: If you tend to overheat, prioritize latex or hybrid models with breathable coil cores and open‑cell foams.
Here’s a quick decision matrix:
| Position | Recommended Type | Ideal Firmness |
|---|---|---|
| Side | Memory Foam or Latex | 3‑5 |
| Back | Hybrid or Medium‑Firm Foam | 5‑7 |
| Stomach | Innerspring or Firm Hybrid | 7‑9 |
Combine this matrix with your temperature needs to narrow the field.
Testing and Buying: A Practical Checklist
- Try before you buy: Lie on the mattress for at least 15 minutes in your normal sleep posture. Pay attention to pressure under shoulders, hips, and lower back.
- Check motion isolation: If you share the bed, have a partner roll or shift to see if the movement travels.
- Measure temperature response: Sit on the surface for a few minutes; it should feel cool or only mildly warm after a minute.
- Review trial policy: A 100‑night at‑home trial lets you return the mattress if sleep doesn’t improve.
- Consider warranty: Look for at least 10‑year coverage on sagging beyond 1.5 inches.
- Factor in delivery: Some brands offer free white‑glove service that removes your old bed, reducing hassle.
When you’ve narrowed the models, compare the total cost of ownership: price, expected lifespan (usually 8‑10 years), and any extra fees for foundations or protectors.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Choosing based solely on price: Cheap mattresses often use low‑density foam that loses shape quickly, leading back to insomnia.
- Ignoring your sleep position: A mattress that feels perfect while you’re sitting may not support your spine when you lie down.
- Overlooking material quality: Look for certifications such as CertiPUR-US (foam) or GOLS (organic latex) to ensure low off‑gassing.
- Skipping the trial period: Even if the showroom feels great, real‑world performance can differ after weeks of use.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you’ve swapped mattresses multiple times and still wake up feeling unrested, it may be time to consult a sleep specialist. Underlying conditions like sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome require medical treatment beyond a new mattress.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should I sleep on a new mattress before judging it?
Give it at least two weeks of regular use. Your body needs time to adjust to the new support system, and most sleep‑related improvements appear after 7‑14 nights.
Is a softer mattress always better for side sleepers?
Generally, a softer surface (firmness 3‑5) relieves pressure on the shoulders and hips, but the mattress still needs enough support to keep the spine aligned. Look for memory foam or latex with zoned support layers.
Can a mattress really impact body temperature?
Yes. Materials that trap heat, like dense memory foam, can raise core temperature by up to 1°C. Latex, hybrid designs with coil cores, or gel‑infused foams promote airflow and keep you cooler.
What warranty length indicates a durable mattress?
A minimum of 10 years is a solid benchmark. Shorter warranties often signal lower‑quality foams that may sag or develop body impressions prematurely.
Should I buy a mattress protector for insomnia?
A breathable, hypoallergenic protector can prevent moisture buildup that makes the surface feel warmer. Choose a thin, moisture‑wicking fabric to avoid reducing the mattress’s cooling properties.
